SQL LIKE OPERATOR TUTORIAL
SQL LIKE OPERATOR
The LIKE operator allows you to use wildcard characters when searching a character field. A wildcard character is one that doesn't match a specific character but instead matches any one character or any of one or more characters.
The LIKE operator selects alphanumeric values with a particular pattern or mask.
SQL LIKE SYNTAX
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name LIKE pattern;
SQL LIKE EXAMPLE
We are going to use our table "publisher3" for this example:
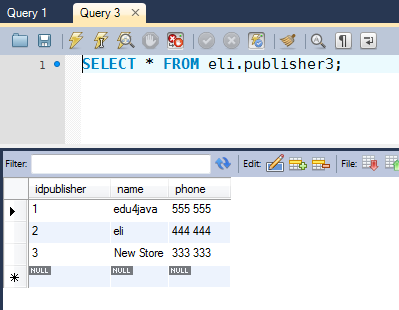
In our exercise we want to select the names of the publishers which end with an "a".
We will use the following SQL statement:
SELECT * FROM eli.publisher3 where name like '%a';
We can use MySQL Workbench to see the following result;
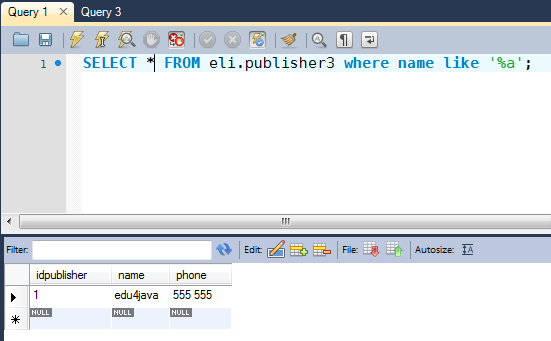
The "%" sign is used to define wildcards (missing letters) both before and after the pattern;
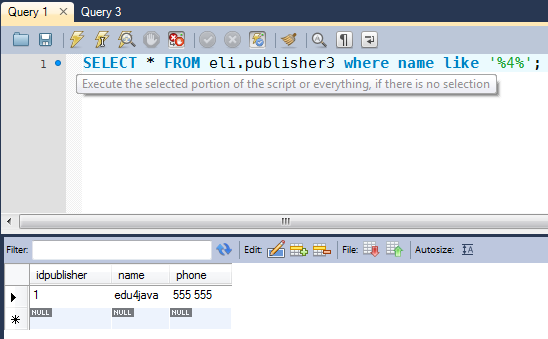
Remember, if you're using MS Access you need to change the percent sign (%) to an asterisk (*):
SELECT * FROM eli.publisher3 WHERE name like '*a';
In some database systems, the LIKE operator is case-sensitive; in others it is not. Oracle, for example, is case-sensitive and SQL, as we can see below, isn´t;
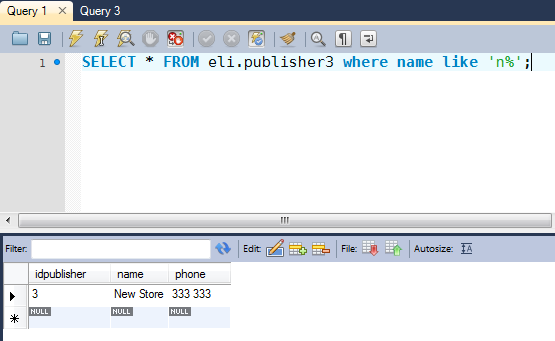
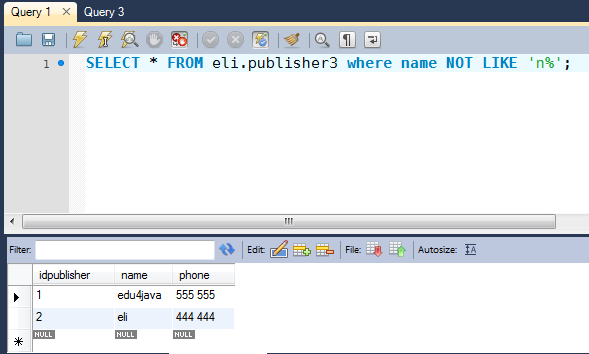
You can also use the NOT operator in concert with the LIKE operator, which produces a match when the character and wildcard combination is not found.
| << Previous | Next >> |



