Video Tutorial 8 SQL. DELETE FROM and TRUNCATE with MySql Workbench
SQL DELETE Statement
The DELETE statement is used to delete rows in a table.
You specify which table to delete the records from, and if required, you add a WHERE clause to specify which records to delete.
Notice that if you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be deleted!
SQL DELETE Syntax
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_column=some_value;
SQL DELETE EXAMPLE
This is our table "publisher3", which we are going to use in our example to delete data;
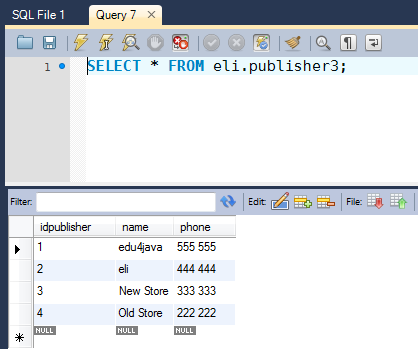
Now we are going to delete the columns with the idpublisher=4";
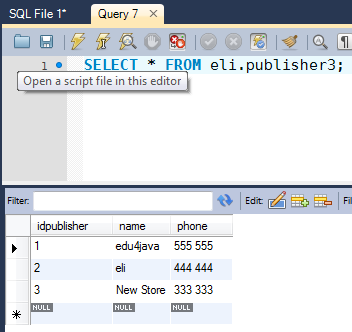
DELETE FROM `eli`.`publisher3` WHERE `idpublisher`='4';
And the result is;
SQL TRUNCATE Statement
Removes all rows from a table without logging the individual row deletions.
TRUNCATE TABLE is similar to the DELETE statement with no WHERE clause; however, TRUNCATE TABLE is faster and uses fewer system and transaction log resources.
SQL TRUNCATE Syntax
TRUNCATE table_name;
SQL TRUNCATE EXAMPLE
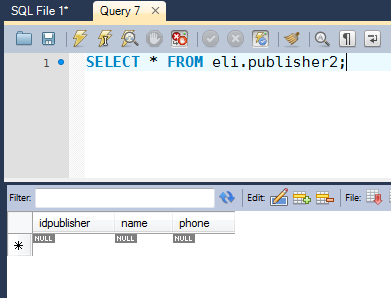
We are going to delete the table "publisher2";
TRUNCATE eli.publisher2;
And this is how our table "publisher2" is now;
| << Previous | Next >> |



